Neurodevelopmental disabilities (NDD) are a group of conditions associated with brain and neurological system functions. NDD are characterized by developmental differences that can cause challenges in areas such as social, personal, academic and/or occupational functioning.
Common forms of NDD include the following (Figure 1):
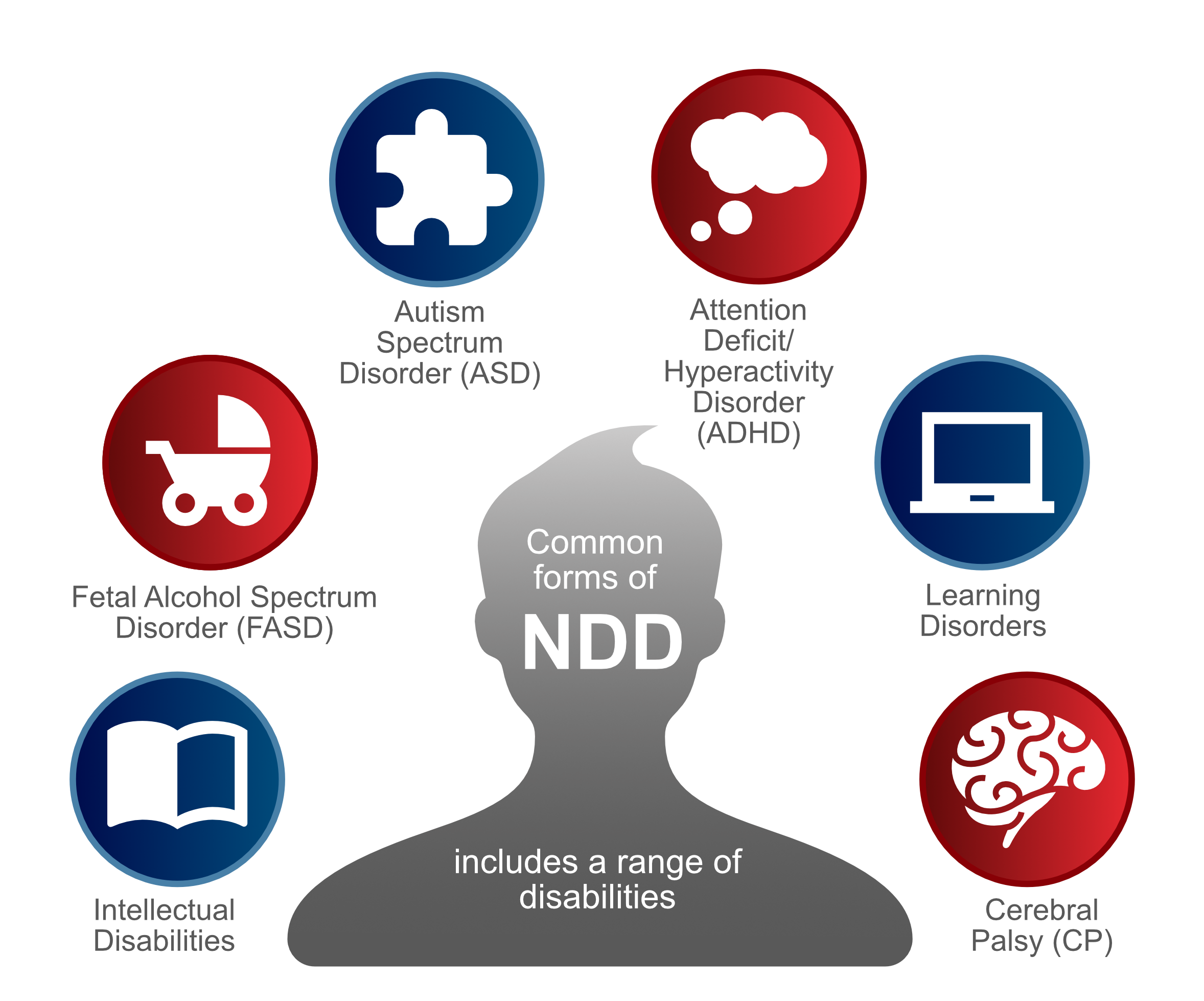
Figure 1: Common forms of NDD
NDD can be thought of as on a continuum of severity with different support needs. Some individuals will experience mild challenges, while others may experience profound challenges requiring more ongoing and/or intensive supports. Challenges can include task-centred impacts, such as difficulty with speech, reading, or mathematics, and/or challenges with a wider impact, such as cognition or general social skills.
NDD begin in childhood with many of these disabilities being detected before a child enters grade school. While the behaviours and symptoms experienced by an individual often
change and evolve as they age, NDD are permanent and can result in lifelong functional challenges.
NDD frequently co-occur, meaning that an individual can experience more than one NDD. The presence of multiple NDD can result in more complex needs requiring more intensive supports.